Automation
Use GraphQL to automate tasks in your app: Execute queries when some event happens, chain queries, and schedule and trigger queries via WP-Cron.

Click to watch tutorial video - 07:19
Use GraphQL to automate tasks in your app:
- Execute queries when some event happens
- Chain queries
- Schedule and trigger queries via WP-Cron
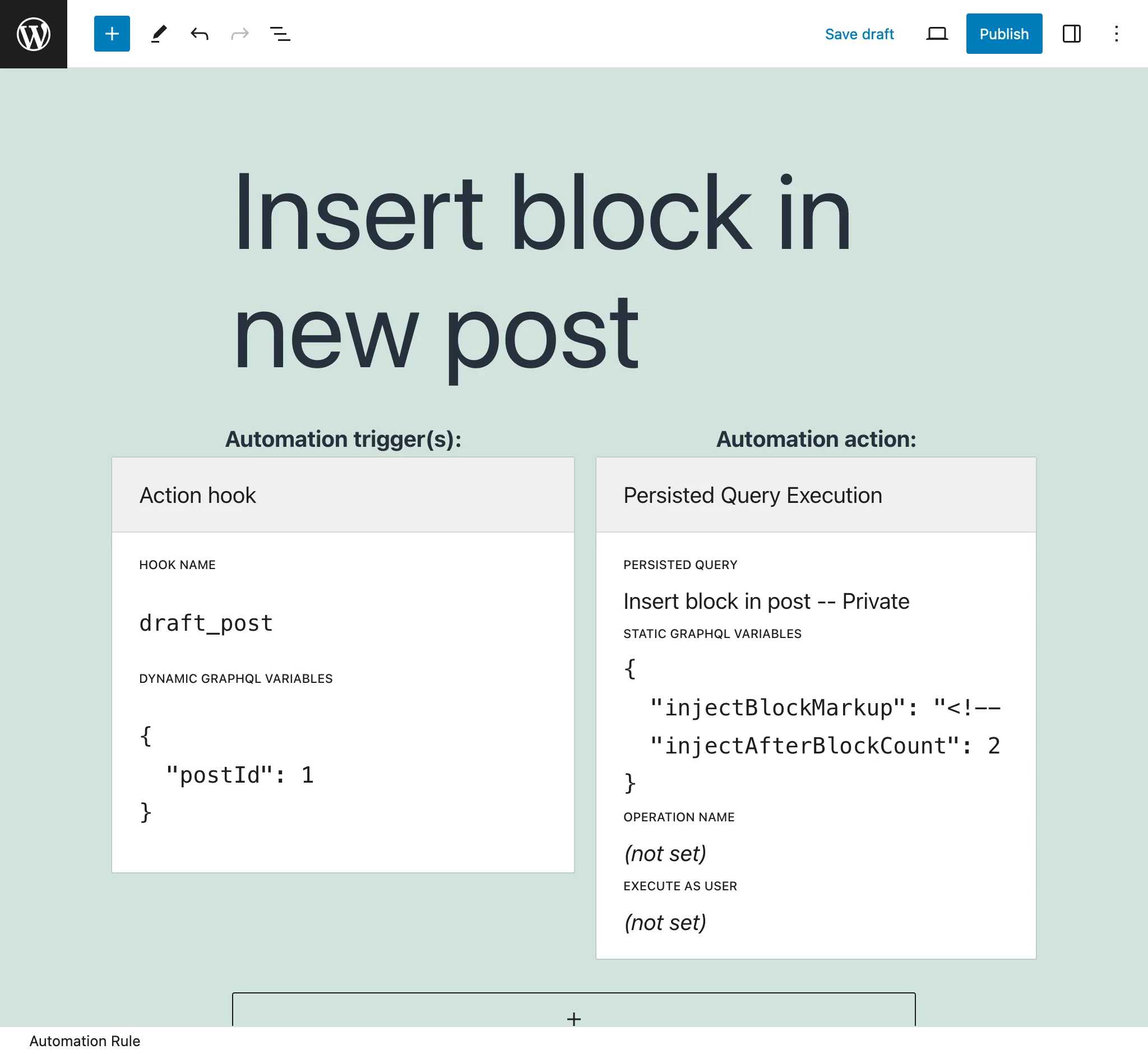
Automation Configurator
Create automations via the WordPress editor, with any WordPress action hook as the trigger, and the execution of a GraphQL persisted query as the action.
Query Resolution Action
When the GraphQL server resolves a query, it triggers the action hook gatographql__executed_query with the GraphQL response, allowing the chaining of GraphQL queries.
WP-Cron
Action hooks are provided to trigger the execution of a GraphQL query every X amount of time:
gatographql__execute_querygatographql__execute_persisted_query



