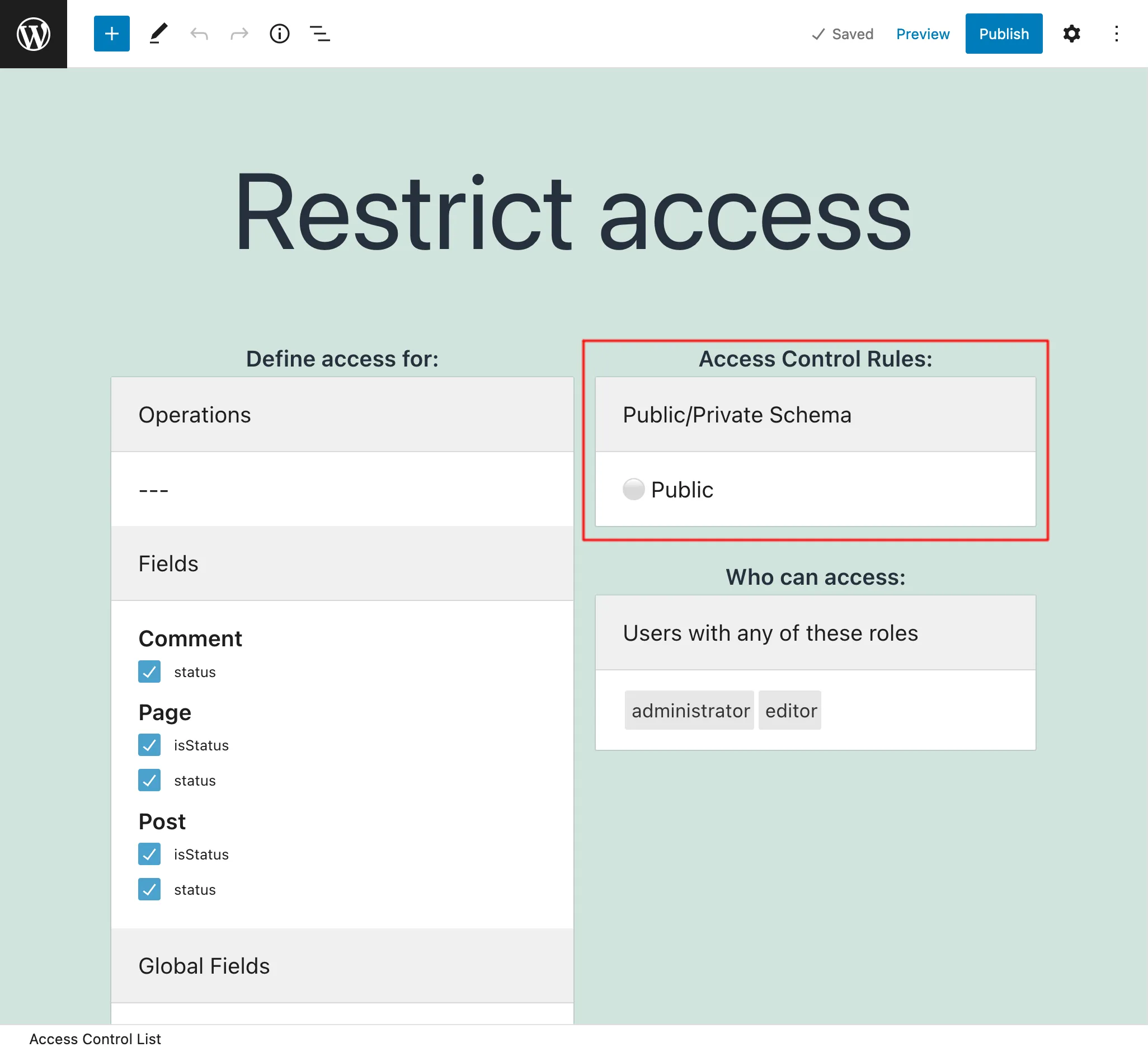
Feature:
Access Control
Access Control
The GraphQL endpoint, which can return any piece of data accessible through the schema, could potentially allow malicious actors to retrieve private information. Hence, we must implement security measures to protect the data.
Access Control
With access control lists, we can define who can access each operation, field and directive in the schema:
- Disable access to everyone
- Grant access if the user is logged-in, or logged-out
- Grant access if the user has some role
- Grant access if the user has some capability
- Grant access if the visitor comes from some IP or IP range
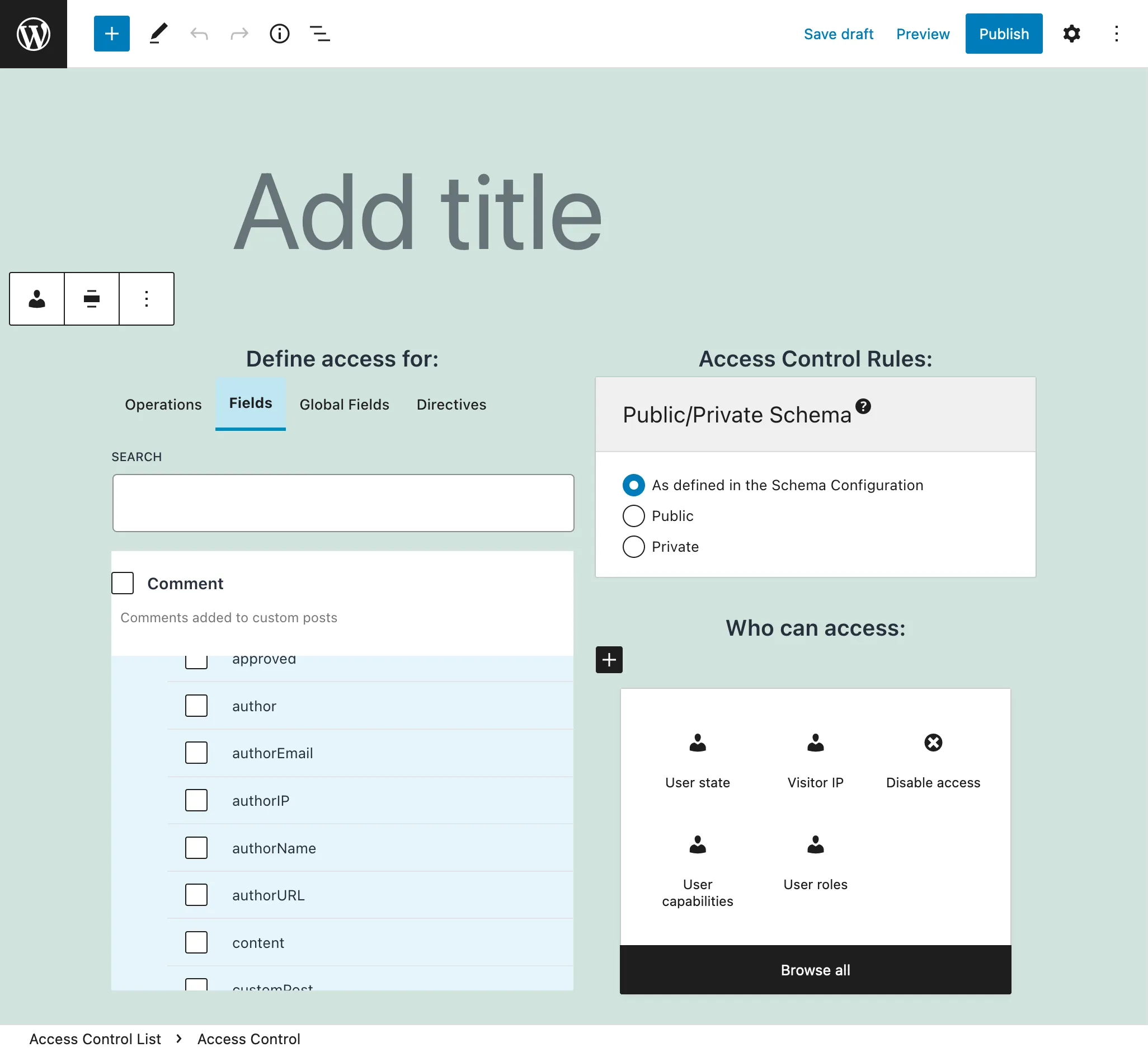
Public/Private Schema
What should happen when a user without access to some field or directive in the schema, attempts to access it?
With the public/private API mode we can control the desired behavior:
In the public API, the fields in the schema are exposed, and when the permission is not satisfied, the user gets an error message with a description of why the permission was rejected.
In the private API, the schema is customized to every user, containing only the fields available to him or her, and so when attempting to access a forbidden field, the error message says that the field doesn't exist.