Feature:
HTTP Caching
HTTP Caching
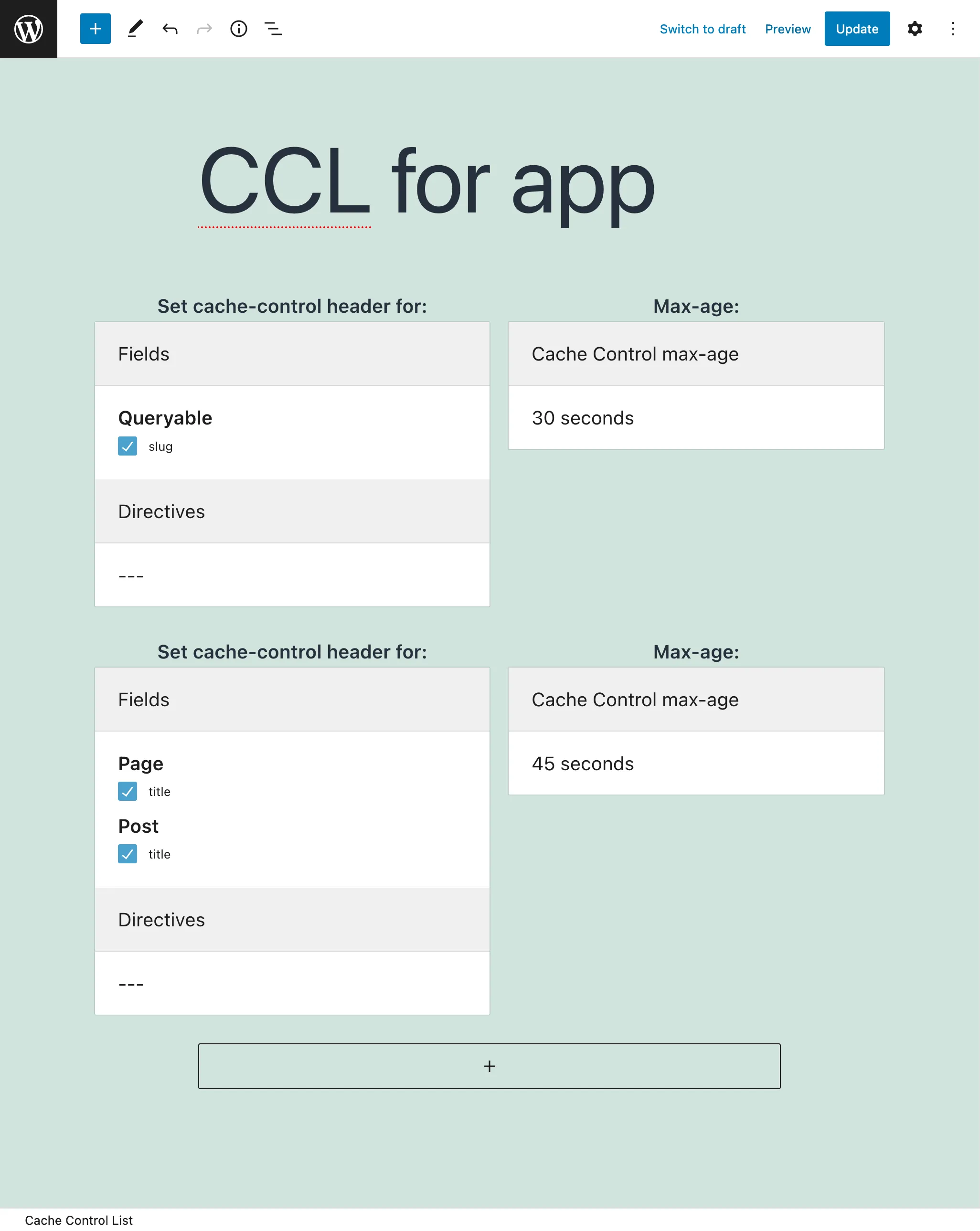
Because it sends the queries via POST, GraphQL is normally not cacheable on the server-side or intermediate stages between the client and the server (such as a CDN), and we need to worry about adding a caching layer on the application on the client-side, making it slower and more complex.
However, whenever accessed via GET (as natural for persisted queries, and using param ?query=... otherwise), their response can be cached through standard HTTP caching.
We can define for how long every field or directive must be cached, and the response will include a Cache-Control header, whose max-age value is calculated automatically from all the fields and directives in the requested query (or no-store if it involves user state).